Before the 1940s, Canada’s capital was still a relatively small city. However, with the onset of World War II, a massive influx of migrants from European countries and other Canadian cities transformed it into a densely populated urban centre. Additionally, the war sparked an industrial boom, elevating Ottawa’s industry to a new level and turning the city into a thriving hub. More on ottawayes.com.
Demographic Changes in Ottawa During World War II
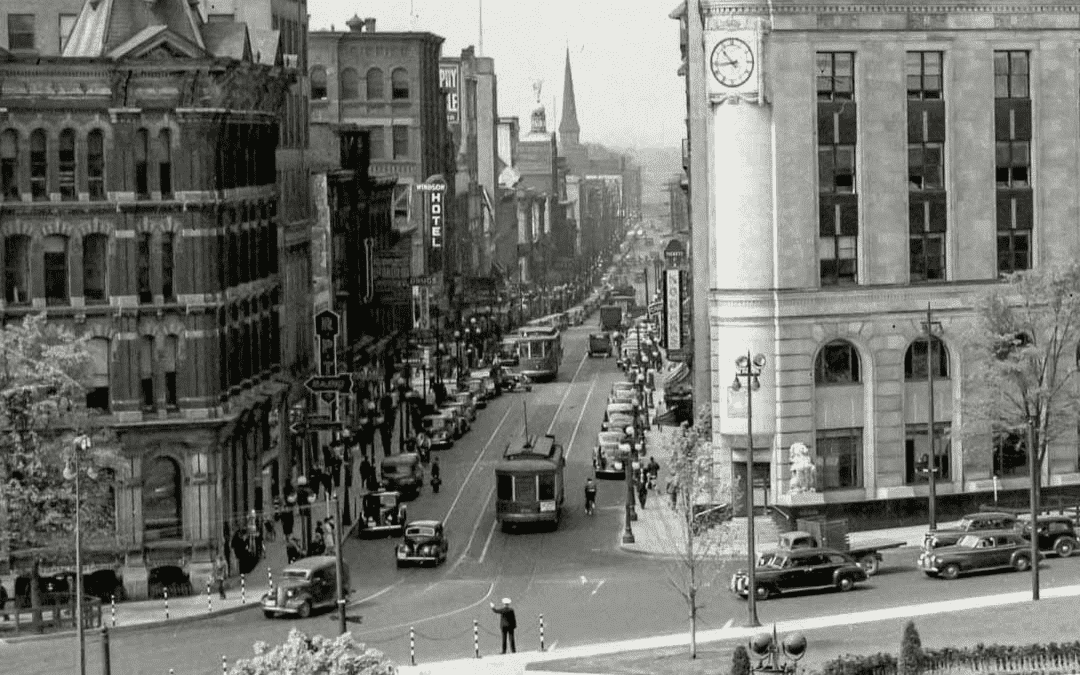
Despite being the capital of Canada, Ottawa’s population before the war was comparable to that of a small provincial town. However, during World War II, this changed significantly. Twenty years before the war, the city’s population was around 100,000. By the early 1940s, it had grown rapidly to over 150,000 residents.
Due to these rapid demographic shifts caused by the war, Ottawa evolved from a small town into a major centre of the country. The city’s population growth between 1939 and 1945 was primarily driven by the continuous arrival of military personnel from other parts of Canada, as well as civilians seeking better job opportunities and a new life in the capital. Additionally, a significant number of European refugees contributed to Ottawa’s population surge. Many people were forced to leave their homes on another continent to escape the horrors of war, and a large number of them settled in Ottawa.
However, many refugees faced significant challenges in the capital. Italian and German immigrants, in particular, experienced distrust, prejudice, and even hostility from Canadians, as people feared they might be supporters of Hitler or Mussolini. Considered a potential security risk, these immigrants were placed in internment camps on the outskirts of Ottawa between 1939 and 1944. In total, there were about 40 such camps across Canada.
Many of these internees were forced to work in physically demanding jobs, including:
- Road construction
- Logging
German and Italian refugees were eventually released from Canadian internment camps in the winter of 1944, allowing them to begin rebuilding their lives.
By the end of World War II, Ottawa’s population had grown tremendously. The city centre was constantly bustling, and traffic congestion became a common sight on the roads.
Industrial Development in Ottawa During World War II
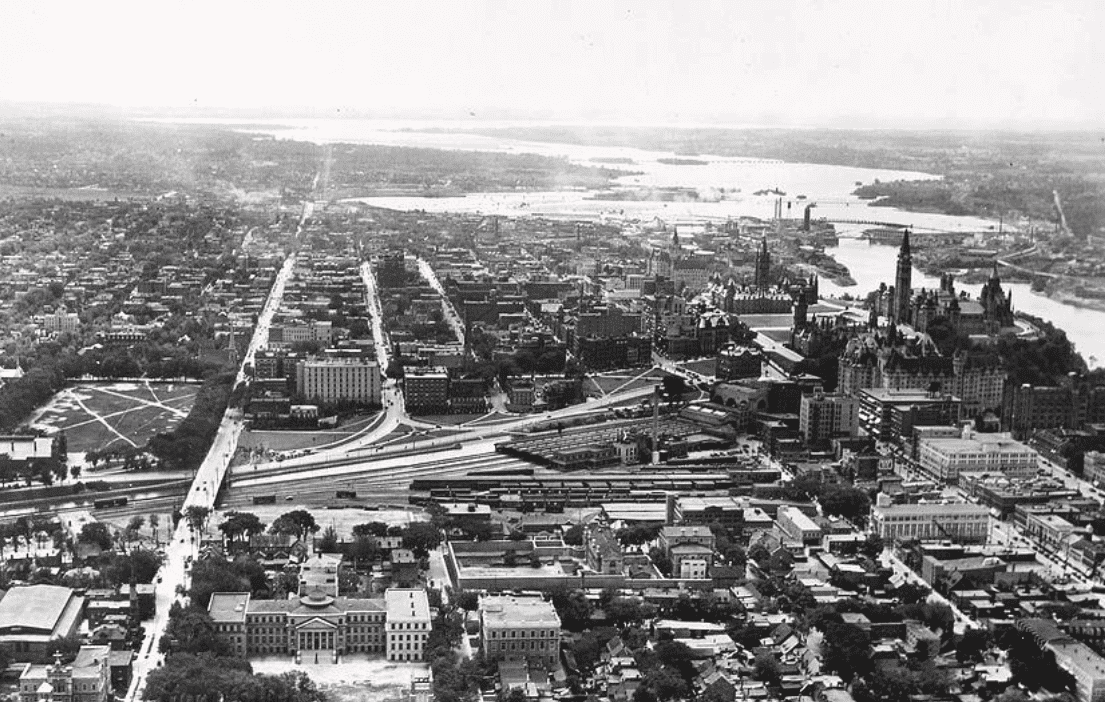

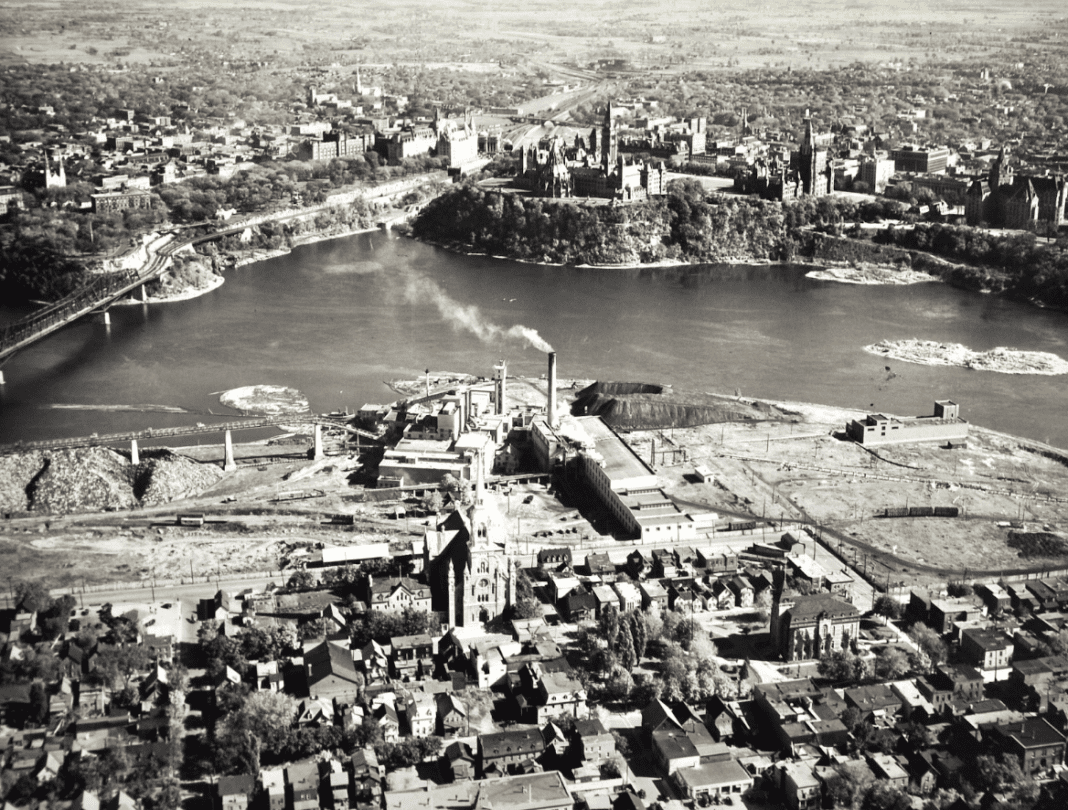
World War II also marked a significant turning point in Ottawa’s industrial sector. The city’s centre expanded rapidly, new housing was constructed for military personnel, and various new manufacturing facilities, including the “Experimental Farm,” were established.
One of the most notable industrial advancements during the war was the opening of the E.B. Eddy factory. The area surrounding the plant became a major industrial zone, attracting thousands of workers every day.
Between 1939 and 1945, Ottawa emerged as a crucial industrial hub supporting the Allied war effort. Factories in the capital produced railway cars, aircraft, and aircraft components. The Ottawa Car Manufacturing Company also played a vital role, specializing in manufacturing bomb bay doors, bomber mechanisms, aircraft wing tips, and many other critical components.
Through these developments, Ottawa solidified its position as a key centre of military and industrial support during World War II, significantly shaping the city’s post-war growth and identity.
